Simulated a microgrid of hybrid PV-wind power system
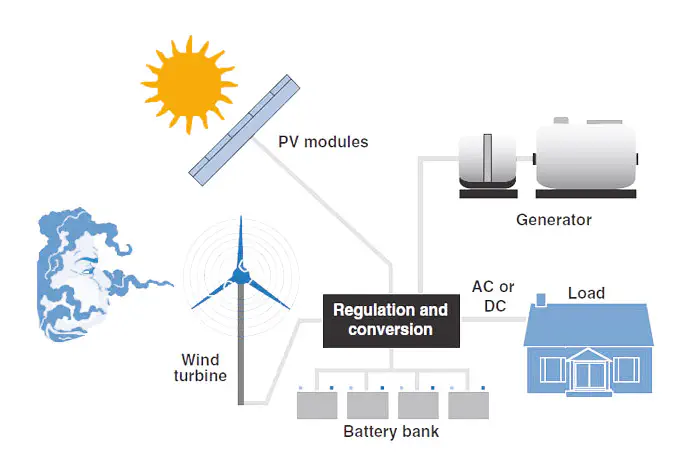 PV-wind power system
PV-wind power systemThe microgrid incorporates three levels of control to manage the power flow between the grid, battery, and the PV-wind power system. This allows for efficient utilization of the generated power, ensuring that surplus energy is not wasted and deficits are adequately supplemented.
At the core of this control system are the mathematical models of the PV array, wind turbine, and battery. These models enable the microgrid to accurately predict and optimize the power generation and storage capabilities of each component. By understanding the behavior and characteristics of these devices, the microgrid can make informed decisions about power distribution and utilization.
Additionally, the microgrid employs various systematic control methods to maintain stability and maximize energy efficiency. One commonly used control technique is the Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) control, which continuously adjusts the power flow based on the difference between the desired and actual power output. This helps regulate the power exchange between the grid, battery, and PV-wind power system, ensuring that energy is neither wasted nor insufficient.
Another important control method used in microgrids is Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT). MPPT algorithms are employed to optimize the power output of the PV array and wind turbine by tracking and maintaining the devices at their maximum power points. By dynamically adjusting the operating conditions, such as voltage or current, the microgrid can extract the maximum available power from the renewable energy sources.
Adaptive control is yet another systematic approach used in microgrids. This control method enables the microgrid to adapt its operation based on changing conditions, such as fluctuations in power generation or load demand. By continuously monitoring and analyzing the system’s performance, the microgrid can adjust its control parameters in real-time, ensuring efficient and reliable operation under varying circumstances.
Overall, the combination of these control methods empowers the microgrid to effectively manage power generation, storage, and distribution. It ensures that excess energy produced by the PV-wind power system is efficiently utilized by either supplying the grid or charging the battery. Conversely, in times of increased demand or reduced power generation, the microgrid can draw power from the battery or the grid to meet local load requirements. This dynamic control strategy enables the microgrid to achieve optimal energy balance, reducing reliance on the main grid and enhancing the overall sustainability and resilience of the power system.
In conclusion, the microgrid’s three levels of control, encompassing mathematical models and systematic control methods like PID control, MPPT, and adaptive control, play a vital role in managing power flow and optimizing the utilization of renewable energy sources. Through these control techniques, the microgrid ensures efficient and reliable operation, enhancing the sustainability and resilience of the power system.